10. Fun with Magnets class 6 NCERT notes Chapter 10 Science download in pdf

Exam Notes: Fun with Magnets
Welcome to Fun with Magnets class 6 NCERT notes Chapter 10 Science NCERT Notes specially created by padhaiguru.in.
Introduction to Magnets
1.1 Exploring Magnetism
- Paheli and Boojho encounter magnets while observing a crane picking up iron from waste material.
- Common items like stickers, pin holders, and pencil boxes have hidden magnets.
- The story highlights the discovery of natural magnets through shepherd Magnes.
Types and Shapes of Magnets
1.2 Types of Magnets
- Natural magnets discovered through shepherd’s experience.
- Natural magnets, like magnetite, attract iron due to their magnetic properties.
- Artificial magnets made from iron have been developed for various uses.
1.3 Shapes of Magnets
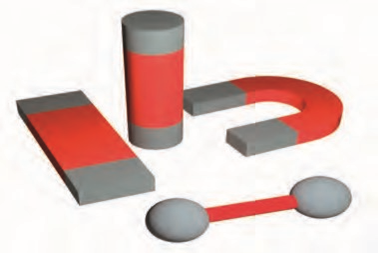
- Magnets come in various shapes: bar magnet, horseshoe magnet, cylindrical magnet, etc.
- Different shapes exhibit different magnetic properties.
- Fig. illustrates various magnet shapes.
Magnetic and Non-Magnetic Materials
2.1 Identifying Magnetic Materials
- Experiment with magnets and objects to identify magnetic and non-magnetic materials.
- Materials like iron, nickel, and cobalt are magnetic; others are non-magnetic.
How Magnets Work
2.2 Attraction and Repulsion
- Magnetic poles explained – North-seeking pole (north) and South-seeking pole (south).
- Bar magnet attracts iron filings; poles attract near the ends.
- Experiment with iron filings shows magnetic field patterns.

2.3 Finding Directions with Magnets
- Magnets used for direction finding since ancient times.
- Emperor Hoang Ti’s chariot example – statue always pointing South.
- Making a simple direction finder using a bar magnet.
Making Magnets and Compass
2.4 Making Magnets
- Method to make magnets by repeatedly moving a bar magnet along an iron bar.
- Compass explained as a device using magnetized needle to find directions.
2.5 Making Your Own Compass
- Creating a compass using an iron needle, cork, and water.
- Observing the consistent direction indicated by the compass needle.
Attraction and Repulsion Between Magnets
3.1 Interactions Between Magnets
- Magnets exhibit both attraction and repulsion.
- Like poles repel, unlike poles attract.
- Experiment with toy cars and magnets to demonstrate these interactions.

Keywords and Definitions
- Magnetite: A natural mineral with magnetic properties, often used to describe rocks with magnetic characteristics.
- Magnetic Poles: The regions on a magnet where its magnetic force is strongest – North and South poles.
- Artificial Magnets: Magnets created by humans, usually by magnetizing a piece of iron or steel.
- Compass: A device with a magnetized needle that aligns with the Earth’s magnetic field, used for finding directions.
- Attraction: The force that pulls two objects together due to their magnetic properties.
- Repulsion: The force that pushes two objects apart due to their like magnetic properties.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
Q1: How were natural magnets discovered?
A: Natural magnets were discovered through a story involving a shepherd named Magnes in ancient Greece. He found his stick being attracted to a rock on a mountainside, which was a natural magnet.
Q2: Can any material be magnetized?
A: Not all materials can be easily magnetized. Iron, nickel, and cobalt are commonly magnetic materials, while materials like plastic or wood are non-magnetic.
Q3: What are the main types of magnets?
A: The main types of magnets include natural magnets (magnetite) and artificial magnets (made from iron or steel).
Q4: How does a compass work?
A: A compass works by utilizing a magnetized needle that aligns with the Earth’s magnetic field. The needle points in the North-South direction.
Q5: How can we identify the poles of a magnet?
A: The poles of a magnet can be identified using iron filings. Iron filings will cluster around the poles, helping to determine their locations.
Q6: What is the significance of magnet shapes?
A: Different magnet shapes have unique magnetic properties, affecting their interactions with other objects.
Q7: How does a magnet attract and repel?
A: A magnet attracts objects made of magnetic materials and repels objects with the same magnetic polarity.
Q8: What is the history of compass use?
A: Compasses have been used for centuries for direction finding. Early travelers suspended natural magnets to determine directions.
Q9: How can we make our own compass?
A: You can make a simple compass using an iron needle, cork, and water, observing its alignment with the Earth’s magnetic field.
Q10: Why are magnet poles marked as North and South?
A: Magnet poles are marked North and South based on their alignment with the Earth’s magnetic field, with North-seeking poles pointing towards the Earth’s North pole.
This was the end of ncert notes on fun with magnets class 6 chapter 10 science.
For more information, refer to NCERT SOLUTIONS, NCERT NOTES, and NCERT BOOKS
