08. Light Shadow and Reflection class 6 NCERT Notes for Chapter 8 Science

Introduction to light shadow and reflection class 6:
light shadow and reflection class 6 is an interesting chapter 8 of science book. Lets learn more about it below ncert notes.
How Do We See Objects? – light shadow and reflection class 6
- Our surroundings are filled with various objects, such as buses, cars, cycles, trees, animals, and more.
- Question: How do we perceive these objects?
- In the absence of light, like during the night or in a completely dark room, objects are not visible.
- When light is introduced, as from a candle or a torch, objects become visible.
- Light is essential for our ability to see objects.
Luminous and Non-Luminous Objects
- Some objects emit their own light, such as the sun and a torch bulb. These are called luminous objects.
- Others, like chairs, paintings, and shoes, are visible when light from a luminous object reaches them and then travels to our eyes.
Transparent, Opaque, and Translucent Objects
- Objects can be categorized as opaque, transparent, or translucent based on their interaction with light.
- Opaque objects do not allow light to pass through them.
- Transparent objects allow light to pass through them clearly.
- Translucent objects allow some light to pass through, but not very clearly.
Activity 1: Testing Transparency -light shadow and reflection class 6
- Collect various objects like an eraser, plastic scale, pen, notebook, paper, and more.
- Observe whether you can see distant objects through each object.
- Record your observations in a table to classify objects as opaque, transparent, or translucent.
Understanding Shadows
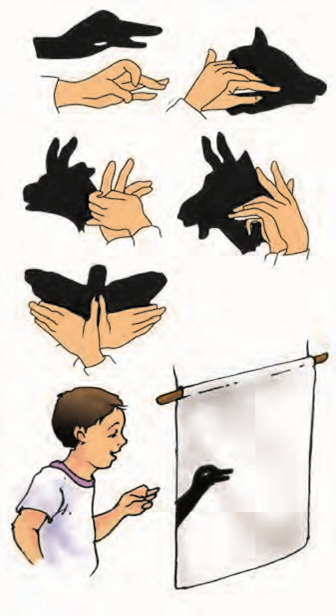
- Shadows are formed when an object blocks the path of light, creating a dark area.
- Question: What are shadows and how do they form?
- Activity 2: Holding opaque objects in sunlight above the ground creates shadows.
- Shadows provide information about the shape of objects.
Activity 3: Investigating Shadows -light shadow and reflection class 6
- In the evening, go to an open ground with a torch and cardboard.
- Shine the torch upwards, creating a light source on your friend’s face.
- Shadows require a source of light and an opaque object to be visible.
- Shadows can be used to identify objects, but they can also be misleading.
Activity 4: Exploring Shadow Characteristics -light shadow and reflection class 6
- Observe shadows cast by a chair on a sunny day.
- Shadow shapes change when objects are turned or moved.
- Compare shadows of different objects, colors, and sizes to study their variations.
Exploring Pinhole Cameras
- A pinhole camera is a simple way to project images.
- Question: What is a pinhole camera and how does it work?
- Activity 5: Creating a pinhole camera using two cardboard boxes.
- Viewing distant objects through the pinhole camera and adjusting for a clear image.
- Pinhole images can be different from shadows and may appear inverted.
Exploring Solar Images with Pinhole Cameras
- Creating a pinhole camera to safely view the Sun.
- During an eclipse, observing the gradual darkening of the Sun’s image.
- Natural pinhole cameras formed by gaps between leaves in trees.
Path of Light and Shadows
- Activity 6: Experimenting with a pipe and candle to understand the straight path of light.
- Light travels in straight lines, causing shadows when obstructed by objects.
- Perceiving objects through pipes and understanding the behavior of light.
Keywords and Definitions:
- Luminous objects: Objects that emit their own light.
- Opaque objects: Objects that do not allow light to pass through them.
- Transparent objects: Objects that allow light to pass through clearly.
- Translucent objects: Objects that allow some light to pass through but not very clearly.
- Shadows: Dark areas formed when light is blocked by objects.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs):
Q1: What are luminous objects?
A1: Luminous objects are those that emit their own light, such as the sun and torch bulbs.
Q2: How are shadows formed?
A2: Shadows are formed when an object blocks the path of light, creating a dark area.
Q3: Can shadows provide information about object shapes?
A3: Yes, shadows give us insights into the shapes of objects, but they can also be misleading.
Q4: How does a pinhole camera work?
A4: A pinhole camera projects images by allowing light to pass through a small hole onto a surface.
Q5: Do shadows appear the same as pinhole images?
A5: Shadows and pinhole images can be different; pinhole images may be inverted and more detailed.
Q6: Can translucent objects create clear shadows?
A6: Translucent objects can create shadows, but they might not be as distinct as those from opaque objects.
Q7: How can shadows mislead us about object shapes?
A7: Shadows can sometimes distort object shapes depending on the angle and direction of the light source.
Q8: Can shadows be cast in complete darkness?
A8: Shadows require a source of light to be visible, so they cannot be cast in complete darkness.
Q9: Why do shadows change when objects are moved?
A9: Shadows change when objects are moved because the angle and direction of the blocking object change.
Q10: Are pinhole images inverted or erect?
A10: Pinhole images are usually inverted, which means they appear upside down.
This was the end of ncert notes on light shadow and reflection class 6 chapter 8 science.
For more information, refer to NCERT SOLUTIONS, NCERT NOTES, and NCERT BOOKS
