01. Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science NCERT Notes for Chapter 1 CBSE

Welcome to Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science NCERT Notes for Chapter 1 CBSE.
Nutrition in Plants – Class 7 Science NCERT Notes
Introduction
In this chapter, we will explore the fascinating world of plant nutrition. Plants, just like humans and animals, need essential nutrients to grow and survive. Let’s delve into the various aspects of nutrition in plants.
The Cell: Building Block of Life
Just as bricks construct buildings, cells are the basic units forming living organisms. These tiny units are typically visible only under a microscope and share common features:
- Cell Structure: Cells are enclosed by a protective membrane called the cell membrane.
- Nucleus: Most cells contain a central structure called the nucleus, acting as the cell’s control center.
- Cytoplasm: Surrounding the nucleus is a jelly-like substance called cytoplasm, where vital cellular processes occur.
Cells, whether simple or complex, serve as the fundamental building blocks of life, sustaining all living organisms.

What is Nutrition?
Nutrition refers to the process of obtaining and utilizing nutrients, which are essential for the growth, development, and maintenance of an organism. In the case of plants, nutrition involves the uptake of nutrients from the environment and their utilization for various life processes.
Modes of Nutrition
Plants exhibit two main modes of nutrition: autotrophic and heterotrophic.
Autotrophic Nutrition
Autotrophic nutrition is the process by which plants produce their food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water through a process known as photosynthesis. This mode of nutrition is exclusive to plants and some microorganisms.
Heterotrophic Nutrition
Heterotrophic nutrition involves obtaining ready-made organic food by consuming other organisms. While this mode is prevalent among animals, some plants also exhibit heterotrophic nutrition.
Photosynthesis – The Key Process
Photosynthesis is the fundamental process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy in the form of glucose. This energy is essential for the plant’s growth and various metabolic activities.
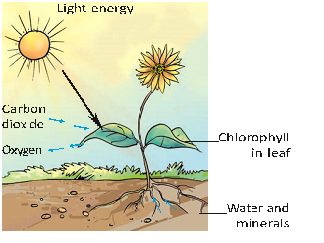
Key Steps of Photosynthesis
- Absorption of Light: Plants have pigments like chlorophyll that absorb sunlight.
- Conversion of Light Energy: Light energy is converted into chemical energy in the form of ATP and NADPH.
- Carbon Fixation: Carbon dioxide is taken from the air and converted into glucose.
- Oxygen Release: Oxygen is released as a byproduct, which is essential for all living organisms.
Nutrients Required by Plants
Plants require various nutrients for their growth. These are classified into two categories: macronutrients and micronutrients.
Macronutrients
- Nitrogen (N): Essential for the formation of proteins and chlorophyll.
- Phosphorus (P): Important for energy transfer and root development.
- Potassium (K): Aids in photosynthesis and overall plant health.
Micronutrients
- Iron (Fe): Necessary for chlorophyll synthesis.
- Zinc (Zn): Involved in enzyme activities.
- Copper (Cu): Important for electron transport in photosynthesis.
Different Colors of Leaves
Leaves display various colors due to the presence of pigments:
- Chlorophyll: Responsible for green color and essential for photosynthesis.
- Carotenoids: Produce yellow and orange hues, visible when chlorophyll breaks down in fall.
- Anthocyanins: Generate red, purple, and blue shades, influenced by environmental factors.
The combination and intensity of these pigments create the diverse leaf colors we see in nature. Factors like soil, nutrients, genetics, and seasons also contribute to leaf color variations.
Other Modes of Nutrition

While most plants are autotrophs, there are exceptions. Some plants do not have chlorophyll and cannot synthesize their food. They rely on other plants for their nutrition and are considered parasites. Additionally, certain plants can trap and digest insects, supplementing their nutrition.
Saprotrophs
Fungi are examples of organisms that do not have chlorophyll and cannot make their food. They obtain nutrients by absorbing them from dead and decaying matter, following a saprotrophic mode of nutrition.
Nutrient Replenishment in Soil
Farmers use manure and fertilizers to replenish the nutrients in the soil. This is essential because plants continually absorb minerals and nutrients from the soil, and without replenishment, the soil becomes deficient in essential nutrients.
Keywords and Definitions
- Nutrition: The process of obtaining and utilizing nutrients essential for an organism’s growth.
- Photosynthesis: The process by which plants convert light energy into chemical energy.
- Autotrophic Nutrition: Obtaining nutrients by producing food through photosynthesis.
- Heterotrophic Nutrition: Obtaining nutrients by consuming other organisms.
- Macronutrients: Nutrients required in large quantities by plants.
- Micronutrients: Nutrients required in small quantities by plants.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What is the main source of energy for plants?
- The main source of energy for plants is sunlight, which is used in photosynthesis.
2. What are macronutrients and give examples?
- Macronutrients are nutrients required in large quantities by plants. Examples include nitrogen (N), phosphorus (P), and potassium (K).
3. Can plants survive without micronutrients?
- While plants require micronutrients in small quantities, they are essential for proper growth and development.
4. Explain the role of chlorophyll in photosynthesis.
- Chlorophyll is a pigment that absorbs sunlight and plays a crucial role in converting light energy into chemical energy during photosynthesis.
5. What is the significance of oxygen release during photosynthesis?
- The oxygen released during photosynthesis is vital for the respiration of all living organisms, including plants.
6. How do heterotrophic plants obtain their food?
- Heterotrophic plants obtain their food by consuming other organisms or organic matter.
7. Why is iron important for plants?
- Iron is essential for chlorophyll synthesis, which is crucial for photosynthesis.
8. Name the three macronutrients required by plants.
- The three macronutrients required by plants are nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
9. What is carbon fixation in photosynthesis?
- Carbon fixation is the process of converting carbon dioxide from the air into glucose during photosynthesis.
This was the end of Nutrition in Plants Class 7 Science NCERT Notes for Chapter 1 CBSE.
For more information, refer to NCERT SOLUTIONS, NCERT NOTES, and NCERT BOOKS .
